Speedtest: Memory manipulation with SysMem Lib

This time something more advanced, memory manipulation.
Each PLC manufacturer has its own library for doing direct memory manipulation. The functions ignore the data type matching and simply copy n characters from one memory area to another.
Most used functions are:
-
memcpy (copies src. memory into dest. memory)
-
memset (sets wanted value to the dest. memory)
-
memcmp (compares two memory areas and returns)
As most of IDEs are built on top of C, these functions are carbon copies of their C equivalents.
Here are a few examples on how to use MemSet, MemCpy in a PLC environment with some examples of the common faults and risk involved. These examples are using Codesys and their MemUtils library.
Memset
Memset allows the program to set the whole memory area provided to a certain value. I find this extremely useful when resetting structs to zero. It requires no additional memory to set a struct and arrays to a value.
//------------RESET STRUCT WITH A EMPTY STRUCT -------------------
vResultStruct1 := cEmptyStruct;
//------------RESET STRUCT WITH MEM SET -------------------
SysMemSet(ADR(vResultStruct2), 16#0 , SIZEOF(vResultStruct2));
Memcpy
Memcpy allows the program to copy the whole memory area provided to another memory area. This has many uses, but one useful use would be parsing arrays into smaller blocks
//------------COPY STRUCT TO ANOTHER STRUCT -------------------
vResultStruct3 := cEmptyStruct;
//------------COPY STRUCT TO ANOTHER STRUCT MEMCPY -------------------
SysMemCpy(ADR(vResultStruct4), ADR(cEmptyStruct) , SIZEOF(cEmptyStruct));
Memcmp
Memcmp allows the program to compare memory areas. The function returns 0 if same, <> if not same. Compared to struct comparison the MemCmp wins on complexity. The function call will work even if the datatype changes.
//------------COMPARE STRUCT TO ANOTHER STRUCT -------------------
//NOTE: Codesys doesn't support complex struct comparing with = <>
vResult5 := vResultStruct3.dummy1 = cEmptyStruct.dummy1
AND vResultStruct3.dummy2[0] = cEmptyStruct.dummy2[0]
AND vResultStruct3.dummy2[1] = cEmptyStruct.dummy2[1]
AND vResultStruct3.dummy2[2] = cEmptyStruct.dummy2[2]
AND vResultStruct3.dummy2[3] = cEmptyStruct.dummy2[3]
AND vResultStruct3.dummy2[4] = cEmptyStruct.dummy2[4]
AND vResultStruct3.dummy2[5] = cEmptyStruct.dummy2[5]
AND vResultStruct3.dummy2[6] = cEmptyStruct.dummy2[6]
AND vResultStruct3.dummy2[7] = cEmptyStruct.dummy2[7]
AND vResultStruct3.dummy2[8] = cEmptyStruct.dummy2[8]
AND vResultStruct3.dummy2[9] = cEmptyStruct.dummy2[9]
AND vResultStruct3.dummy2[10] = cEmptyStruct.dummy2[10]
AND vResultStruct3.dummy2[11] = cEmptyStruct.dummy2[11]
AND vResultStruct3.dummy4 = cEmptyStruct.dummy4
AND vResultStruct3.dummy5 = cEmptyStruct.dummy5
AND vResultStruct3.dummy6 = cEmptyStruct.dummy6
AND vResultStruct3.Elem1 = cEmptyStruct.Elem1
AND vResultStruct3.Id = cEmptyStruct.Id
AND vResultStruct3.IdText = cEmptyStruct.IdText;
//------------COMPARE STRUCT TO ANOTHER STRUCT MEMCMP -------------------
vResult6 := SysMemCmp(ADR(vResultStruct4), ADR(cEmptyStruct),SIZEOF(cEmptyStruct)) = 0;
Speed measurements
While the speed of execution is roughly the same, SysMemLib wins in many cases, especially with comparing structs and arrays as Codesys doesn’t support this out of the box.
In some cases, manual struct compare is faster if your application has predictable data. With predictable data you can check the data that is more often changing for comparison. This does require the data type to never change or function updated if it does.
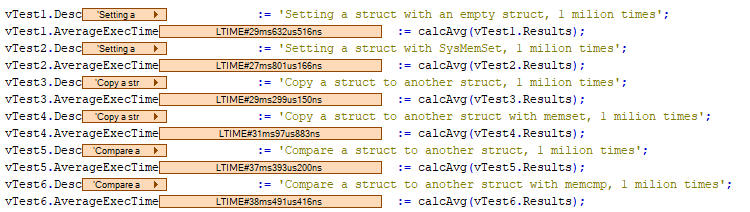
| Measur. | Time took (ms) | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Reset struct with a empty struct First index | 29.6 | Loses as we have to have more memory allocation |
| Reset struct with MemSet | 27.801 | Roughly same speed as empty struct |
| Copy a struct to another struct | 29.3 | |
| Copy a struct to another struct (MemCpy) | 31.09 | Roughly same speed as struct assignment |
| Compare a struct to another struct | 37.4 | Loses on lines of code and flexibility |
| Compare a struct to another struct (MemCmp) | 38.4 | Same call even if modifed data type |
As always, the complete source code is on my github repository dedicated to speed testing.
Related posts in this category
Speedtest: Converting BOOL[1..32] to BYTE[1..4]
Speedtest: Calculations inside loop declarations